Biology : Biodiversity
Introduction to Biodiversity
Biodiversity is defined as the variation of living forms on earth which includes plants, animals, and microorganisms, contain genes, and form a complex ecosystem.
- Total number of biodiversity- 13 million
- Identified biodiversity- 1.75 million
Biodiversity describes the diversity of life at the following three biological levels:
Species diversity:
Species diversity is the component of biodiversity which is a group of plants or animals that are similar and able to breed and produce viable offspring under natural conditions.
Genetic diversity is the level of biodiversity that refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of the species and recessed in all of the individuals that comprise a particular species.
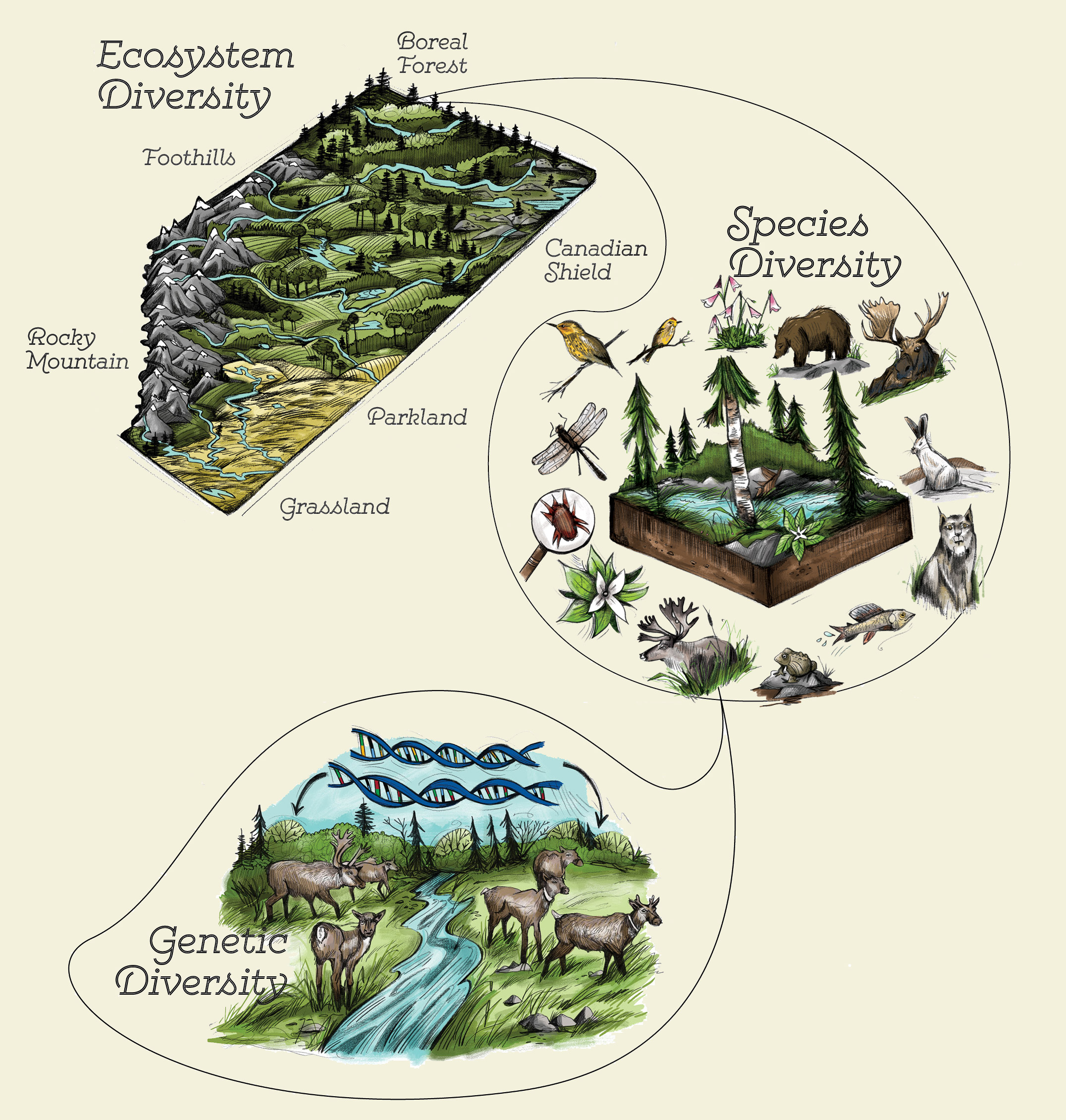
Ecosystem diversity:
Ecosystem diversity is the variation of habitats, community types, and abiotic environments present in a given area. Ecosystem diversity is evaluated through measures of the diversity of the component species.
Benefits of biodiversity
- By protecting biodiversity, we are able to find a new source of food and drink.
- A significant proportion of drugs is derived directly or indirectly from biological sources.
- A wide range of industrial materials i.e. dyes, fibers, resins, etc. are derived directly from biological resources.
- The natural beauty provided by biodiversity inspired composers, artists, and poets.
- Ecosystem and ecological processes play an important role in the breakdown and absorption of pollutants.
- Biological diversity helps in the formation and maintenance of soil texture and the preservation of moisture and nutrients.
- Natural pesticides using biodiversity are in many ways superior to their artificial chemical pesticides.
- Biodiversity also has great importance as a direct source of income and economic development.
Scope of Biodiversity
Tourism:
The total number of species which are found on the earth's surface is called biodiversity. Every species is different from each other. So, the tourist is attracted to them and are willing to know about them in detail which helps to develop tourism in the country. The increase in tourism means an increase in the country's economy.
Scientific research and investigation:
Biodiversity is also important for scientific research and investigation. With the help of biodiversity, the scientist can find out or research scientific things.
Medicine:
Every biodiversity is important in itself. From plants, we can discover various medicines used for various diseases. Medicines that are newly discovered are first observed on animals. So, we can say medicine is also one of the scopes of biodiversity.
Agricultural production:
The food product which we eat daily is obtained from the environment. With variations in these products, we get a variety of food.
Balance of ecosystem:
Biodiversity helps to maintain the ecological balance necessary for survival for not only plants and animals but also humans on earth because they depend on each other directly or indirectly for food.
Floral Diversity of Nepal
|
Group of organism |
Nepal (Known so far) |
Global |
Nepal Representation (%) |
|
Bacteria |
NA |
3,000 to 4,000 |
|
|
Lichens |
465 |
20,000 |
2.3 |
|
Fungi |
1,822 |
69,000 |
2.4 |
|
Algae |
687 |
26,000 to 40,000 |
2.6 |
|
Bryophytes |
853 |
16,600 |
5.1 |
|
Pteridophytes |
534 |
11,300 |
4.7 |
|
Gymnosperms |
27 |
529 |
5.1 |
|
Angiosperms |
5,856 |
220,000 |
2.7 |
|
Platyhelminthes |
168 |
12,200 |
1.4 |
|
Spiders |
144 |
73,400 |
0.2 |
|
Insects |
5,052 |
751,000 |
0.7 |
|
Butterflies and Moths |
6,402,253 |
112,000 |
2.6 |
|
Fishes |
182 |
18,150 |
1.0 |
|
Amphibians |
77 |
4,184 |
1.84 |
|
Reptiles |
118 |
6,300 |
1.87 |
|
Birds |
863 |
9,040 |
9.53 |
|
Mammals |
181 |
4,000 |
4.52 |
Things to remember
- Biodiversity is defined as the variation of living forms on earth which includes plants, animals, and microorganisms, contain genes and form a complex ecosystem.
- Ecosystem diversity is the variation of habitats, community types, and abiotic environments present in a given area.
- Biological diversity helps in the formation and maintenance of soil texture and the preservation of moisture and nutrients.
- Biodiversity also has great importance as a direct source of income and economic development.
- Biodiversity is also important for scientific research and investigation.
- It includes every relationship established among the people.
- There can be more than one community in a society. Community smaller than society.
- It is a network of social relationships that cannot see or touched.
- common interests and common objectives are not necessary for society.

Comments